Nuclear Reactor in South Korea Generates Power Seven Times Hotter than the Sun’s Core
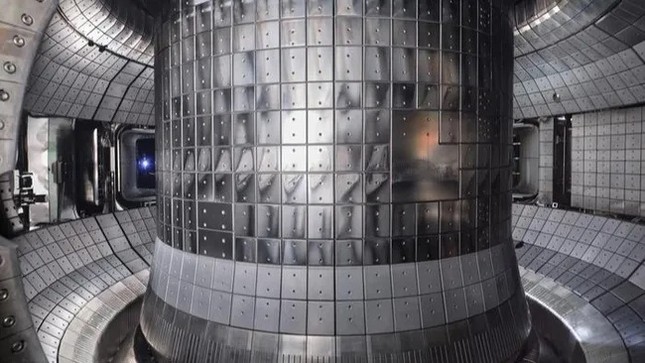
The advanced superconducting Tokamak nuclear reactor in South Korea, known as KSTAR, has broken the previous world record of 31 seconds, which it had set in 2021.
This breakthrough is a remarkable step towards achieving almost limitless clean energy. KSTAR has successfully sustained a temperature of 100 million degrees Celsius for 48 seconds, while the core temperature of the Sun is only 15 million degrees Celsius.
The most common design for nuclear reactors, called tokamak, operates by heating plasma (one of the four states of matter, consisting of positive ions and negatively charged free electrons) and confining it inside a doughnut-shaped reactor chamber with a strong magnetic field.
To extend the duration of plasma burning, scientists have made adjustments to the reactor’s design, including replacing carbon with tungsten to improve the efficiency of the tokamak’s divertor, which helps extract heat and ash from the reactor.
KSTAR’s goal is to maintain a temperature of 100 million degrees Celsius for 300 seconds by 2026. Experts hope that nuclear reactors can be used to generate limitless carbon-free electricity.
[source](Business Today)
